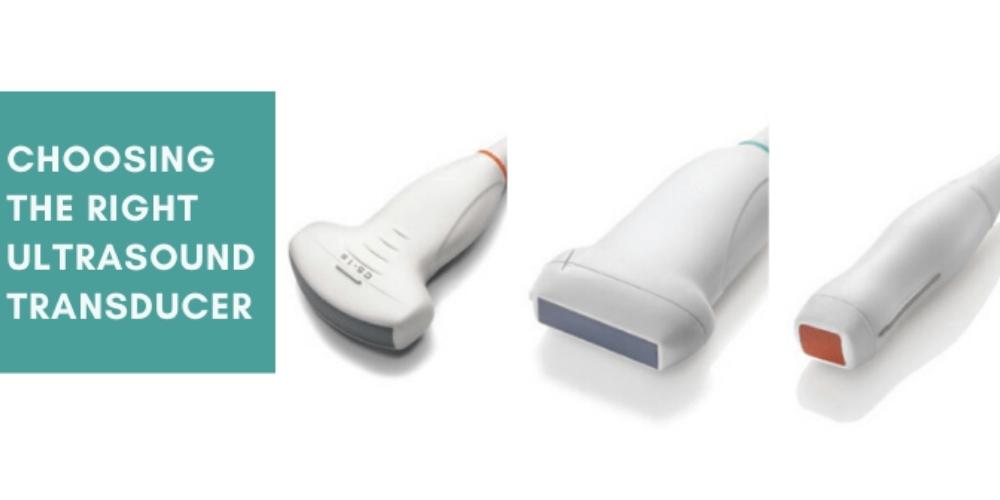
Ultrasound imaging is one of the most widely used imaging modalities. The ultrasound transducer, also referred to as a probe, is the device used to produce the ultrasound image.
The transducer works by producing sound waves that bounce off body tissues and create echoes. The device then receives the echoes and transmits them to a computer that converts them into an image called a sonogram.
Ultrasound imaging is used in a variety of medical contexts, ranging from OB/GYN applications to surgical applications.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, ultrasound has been used to diagnose and examine patients. This is particularly due to the ability to perform ultrasound scans at the patient’s bedside, thereby reducing the risk of spreading the disease.
Moreover, ultrasound is not confined to an imaging suite and is radiation-free, unlike other imaging modalities such as MRI and CT scans. As a result, ultrasound offers medical imaging professionals a safe and quick option in certain cases, although it has its limitations.
Each ultrasound probe is tailored to a specific imaging application; therefore, it is important to understand the difference between each type and the benefits each offers.
Ultrasound Transducer Types
There are a wide variety of ultrasound transducers available today to meet the needs of medical imaging professionals.
In accordance with the needs of each ultrasound procedure, transducers come in different configurations and sizes. Each one provides different features that are tailored to the needs of the practitioner and the nature of the procedure.
Ultrasound transducers that are used to scan over the surface of the skin are referred to as external (or surface) transducers. In contrast, ultrasound probes designed for insertion into an orifice, such as the vagina or rectum, are referred to as internal transducers.
In addition, ultrasound probes vary in design based on piezoelectric crystal arrangement, frequency, and aperture (footprint).
In this article, we will discuss three of the most common ultrasound transducer types linear, convex (standard or micro-convex), and phased array.
Linear Transducers
One of the main features of a linear ultrasound transducer is its linear piezoelectric crystal arrangement. The shape of the probe’s beam is rectangular and it offers an adequate near-field resolution.
Depending on whether the linear transducer is for 2D or 3D imaging, the footprint, applications, and frequency may change.

The linear transducer for 2D imaging has a wide footprint and its central frequency is 2.5Mhz to 12 Mhz. This transducer can be used for a variety of applications, such as:
- Vascular examination
- Venipuncture
- Thyroid
- Breast
- Tendon
- Intraoperative, laparoscopy
- Photoacoustic imaging, ultrasonic velocity change imaging
- To measure thickness of body fat
- Locomotive syndrome check
The linear transducer for 3D imaging also has a wide footprint and a central frequency of 7.5MHz to 11 MHz. This probe can be used for the following applications:
- Breast
- Thyroid
- Arteria carotis of vascular application

Convex Transducers
Convex ultrasound transducers are also referred to as curved transducers due to their curvilinear piezoelectric crystal arrangement.
In addition, the shape of the beam is convex. This type of probe is excellent for in-depth examinations. However, the image resolution of the convex transducer decreases as the depth increases.

Like the linear transducer, the footprint, applications, and frequency of convex probes also depends on whether the product is for 2D or 3D imaging.
The 2D imaging convex probe has a central frequency of 2.5MHz to 7.5MHz and a wide footprint. It can be used for diagnosis, examination, and other ultrasound-guided procedures, such as abdominal exams.
The 3D imaging convex transducer has a central frequency of 3.5MHz to 6.5MHz and provides a wide view. It can be used for abdominal examinations.
Convex probes also have a subtype called micro convex probes. These have a much smaller footprint and are more commonly used in neonatal and pediatric settings.

Phased Array Transducers
This ultrasound transducer is named after its piezoelectric crystal arrangement: phased array. This is the most commonly used crystal arrangement.
Phased array probes have a small footprint and a low frequency of 2MHz to 7.5MHz. It has a narrow beam point which expands depending on the applied frequency. Their small footprint makes them an ideal fit for cardiac applications due to their size and ability to examine a large area without having to move the transducer.
Phased array probes have an almost triangular beam shape and a poor near-field resolution. They are used for multiple types of examinations, such as abdominal, cardiac, and brain exams.

Other Transducer Types
Additionally, medical imaging practitioners have a variety of other transducers at their disposal to meet the needs of their ultrasound-guided procedures.

Endocavitary transducers are commonly used in internal examinations of the patient. They are designed to fit into specific body orifices. These transducers include endocavity transducers. Endocavitary ultrasound probes can be used for different types of ultrasound-guided procedures, including prostate biopsies, and transvaginal and transrectal exams. . These transducers tend to have small footprints and their frequency can vary from 3.5MHz to 11.5MHz. Due to the nature of the procedures they are used for, endocavitary probes are usually protected with a sterile endocavity probe cover. These covers reduce the risk of transmission of healthcare-associated infections and also prevent the ultrasound probe from being contaminated.

Furthermore, transesophagael (TEE) probes are also used for internal examinations. They have a small footprint and are often used for cardiological applications. Cardiologists will typically use the TEE probe to obtain a better image of the heart through the oesophagus. Practitioners may cover these probes with TEE probe covers to protect the patient and reduce the risk of cross-contamination. TEE probes have a frequency of 3MHz to 10MHz.

Physicians and medical imaging staff should take into account the unique features of each ultrasound probe. Depending on the needs of the patient and the ultrasound-guided procedure, practitioners will have to consider the best probe to successfully perform the exam.
Learn more about EDM's comprehensive ultrasound supply and accessory solutions here.