With the increasing demand for ultrasound imaging in the healthcare field, it has become essential for medical students and practicing professionals to master ultrasound interventional techniques. This is where ultrasound training phantoms come into play. Ultrasound training phantoms enhance medical education by providing a realistic and safe environment for healthcare professionals to hone their skills. In this article, we explore the benefits of using ultrasound phantoms for medical students and how they are improving learning outcomes for actively-practicing medical professionals.
The use of ultrasound-guided needle placement is a well-established medical procedure that has been shown to significantly reduce complications and improve the success rate of needle punctures in clinical trials. Adequate visualization of the needle tip via the use of ultrasound increases the success rate of interventions compared to blind methods.
However, according to a study published in the European Society of Radiology in 2015, students typically have limited opportunities for hands-on experience, especially during their study period because of the lack of realistic practice sessions.
“Trial and error” scenarios for minimally invasive procedures like catheter placement in critical care patients are not appropriate for inexperienced staff or students. Moreover, learning time is limited, which makes training or teaching tools such as phantom ultrasound models essential for students, residents and even if you’re already a doctor.
Besides being used for training purposes, in the article The Role of Phantoms in Diagnostic Ultrasound Quality Assurance, the author G. Wayne Moore, explains that phantoms for ultrasound Imaging are also used to test, calibrate and assess the performance of ultrasound machines.

Different Types of Ultrasound Practice Phantoms
Ultrasound phantoms come in various forms, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. They are also made from different materials, ranging from silicone to water-based gels, and even human cadaveric tissue.
| Material | Pros | Cons |
| Commercial Phantom Ultrasound Models or Ultrasound Training Phantoms | Portable Realistic No infection risks Large scanning surface Long shelf-life Reusable | Higher cost Cannot embed additional targets |
| Animal models | Realistic Can embed parts | Short shelf-life Messy Infection risks |
| Tofu | Simple, affordable, portable. Complexity degree can be changed. Target can be inserted but not embedded | Less available Fragile Seeps water Needs refrigeration Uniform echogenic Infection risks |
| Gelatin | Cheap and portable Large scanning surface Injectable targets can be embedded Appearance and shape can be moldable | Requires refrigeration Needs to be prepared Needle tracking Uniform appearance Fragile |
| Agar | Targets can be embedded Portable | Organic based Less available Expensive Needs to be prepared |
| Silicone | No infection risks | Expensive Each needle pass creates a memory in the model |
| Cadaver | Anatomical relevant | Infection risks Storage issues Less available |
| Computer based/Virtual Reality | No infection risks Level of complexity can be modified | Expensive IT support Not portable Inaccurate haptics |
Most Common Ultrasound Training Phantoms
Anesthesia Training Phantoms: These models are a versatile and essential tool for medical professionals seeking to improve their skills in regional anesthesia, nerve block, and vascular access training. These training phantoms often come with a dual-purpose design that features nerves and vessels, which make them serve as a vascular access ultrasound phantom for ultrasound-guided vascular access and also for regional anesthesia peripheral nerve block training.
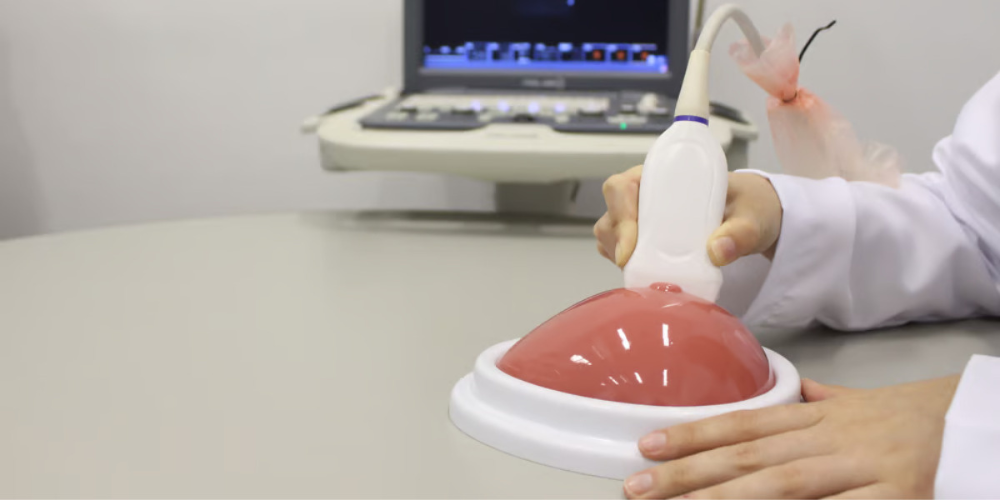
Breast Biopsy Training Phantom: These tissue mimicking-phantoms are crucial for medical professionals and students that aim to enhance their ultrasound-guided breast biopsy skills. Ultrasound breast phantoms replicate the human breast, enabling practitioners to practice and refine their skills in a safe environment with a realistic and accurate representation of what it is like to perform a biopsy on an actual patient.
Thyroid Biopsy Training Phantom: This one is a popular choice among residents and practitioners that want to improve their performance when doing ultrasound-guided fine-needle biopsies of the thyroid gland. They are designed to have a highly realistic feel in ultrasound imaging and should contain the main gland and all surrounding structures, including the right and left lobes and trachea. Additionally, some thyroid training phantoms come with several lesions with varying levels of echogenicity, enabling clinicians to practice their skills.
Universal NAV Training Phantom: These tissue-mimicking models are a go-to tool for medical professionals seeking to improve their ultrasound-guided procedures’ accuracy and safety. These training phantoms feature nerves, arteries, and veins, which are randomly placed at different depths, making it ideal for vascular access training, nerve blocks, and regional anesthesia.
How Ultrasound Training Phantoms Benefit Residents

Ultrasound training phantoms provide a safe and realistic way for healthcare professionals to master ultrasound techniques. Many of the advantages of these tissue-mimicking models include the increase of hands-on experience, improvement of diagnostic and interventional skills, a better understanding of anatomy and physiology, and the reduction of the need for live patients during training.
Increase of Hands-On Experience
In a study published in the Indian Journal of Surgery in 2023, researchers measured the effectiveness of a brief teaching scenario using a phantom-based learning model focused on ultrasound-guided vascular access.
The data collected by the authors shows that a condensed didactic lecture and supervised hands-on training session using phantom ultrasound models had a significant positive impact on the ability to establish ultrasound-guided vascular access. The results revealed that procedural times for ultrasound visualization and the number of cannulation attempts significantly decreased, indicating improved practical proficiency among the student group. Additionally, the success rate of ultrasound-guided endoluminal guide wire placement increased from 36.4 to 100%, demonstrating that every student was able to perform the procedure successfully using this method.
Improvement of Diagnostic Skills
Similarly to the previous research, another group of investigators published a study in Ultrasound in 2020 that aimed to determine the impact of using a lower extremity venous ultrasound phantom in addition to standard teaching methods.
Participants in the study were first-year diagnostic medical sonography students with minimal scanning experience. They were divided into two groups. Group 1 underwent a typical didactic lecture alongside a scan lab assessment where they conducted a venous examination of the lower extremity on a living volunteer.
On the other hand, Group 2 received the same standard didactic lecture as Group 1 and participated in three scheduled scanning sessions on an anatomic lower extremity venous phantom with flow.
Following this, they underwent the same scan lab assessment as Group 1, where they performed a venous examination of the lower extremity on a living volunteer. On day four of the study, scan lab assessments revealed a significant difference in scanning performance and confidence scores, particularly in imaging calf veins, between the two groups.
After the didactic lecture, Group 1’s confidence levels decreased compared to their confidence levels after the scan lab assessment. Conversely, Group 2’s confidence levels increased following the scan lab assessment.
The results of this study suggest that anatomical phantoms can be effectively used to enhance scanning diagnostic skills and increase confidence in ultrasound imaging of lower extremity venous structures.
Better Interventional Performance

Another benefit of the use of ultrasound training phantoms is the improvement of performance in interventional procedures. Authors of a study published in the American Journal of Roentgenology in 2016 explain that simulation-based training is increasingly being used to train novices, especially for technically demanding procedures like carotid artery stenting and laparoscopic surgeries.
However, traditional radiology training methods mostly follow an apprenticeship model which may lead to a marked variation in the quality of training among residents and residency programs. This highlights the need for alternative training methods such as ultrasound training phantoms.
In the same article, the authors collected data to prove that a short 30-minute training session using an abdominal training phantom can enhance technical skills in ultrasound-guided biopsy procedures. Practicing with phantoms for ultrasound imaging resulted in improved simulated biopsy procedure time with 92.3-second reduction, fewer skin punctures that represented a 50% improvement, and fewer needle adjustments with an enhancing percentage of 66%.
Reduction of the Need for Live Patients
Students who want to learn how to execute ultrasound-guided procedures can either participate in cadaver workshops or obtain real-time experience on patients. However, these approaches face various practical difficulties and ethical concerns.
Authors of an article published in Medicine in 2018 explain that commercially manufactured phantoms are an effective alternative that allows students to practice needle placement easily and safely. As we mentioned before, these ultrasound phantoms have a variety of anatomical features and can be used multiple times.
Practicing with training ultrasound phantoms improves trainee confidence and performance and is recommended by experts to achieve proficiency in sonography.

An adequate training in ultrasound image acquisition and interpretation, as well as real-time use of the technology, is imperative for developing motor skills and gaining haptic feedback in students. Simulation using ultrasound training phantoms or tissue-mimicking models has been shown to be an effective tool for teaching these skills, providing nonthreatening practice opportunities and improving student confidence levels.
Additionally, the presence of an experienced instructor during simulation sessions can add value by providing more feedback and answering questions in real-time. Furthermore, simulation training has the potential to assist students who need more time to master their scanning skills, ultimately leading to greater confidence and a better preparedness for entry into the clinical environment.